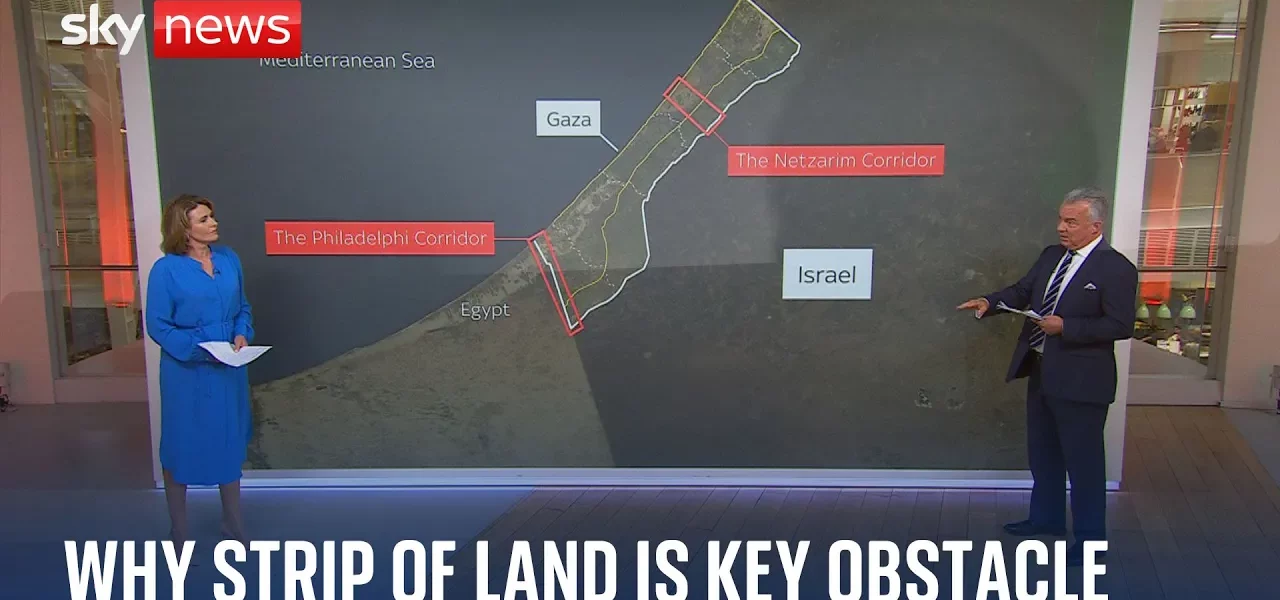
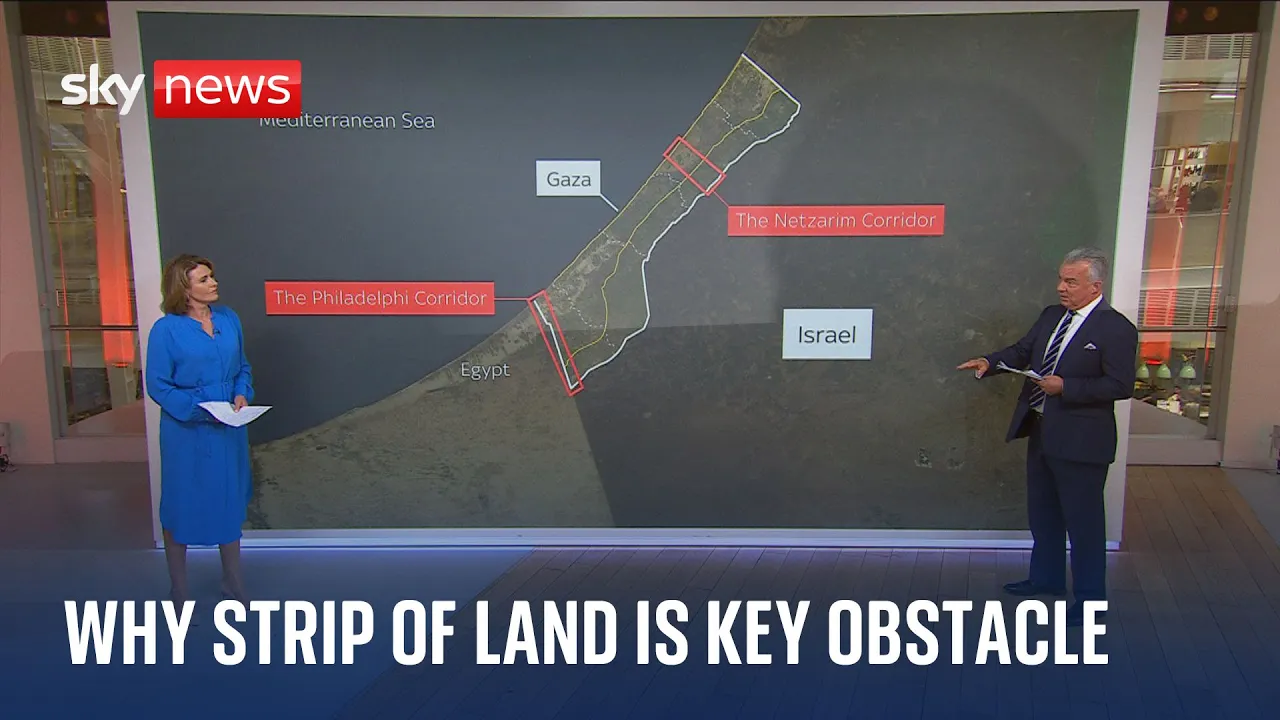
The Philadelphia Corridor: A Detailed Analysis of Its Role in the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
This article provides an extensive overview of the Philadelphia Corridor, exploring its historical background, strategic importance, and current implications in the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas, as discussed by military analyst Shan Bell.
Introduction
The Philadelphia Corridor, a narrow strip of land separating Egypt and Gaza, has become a focal point in the complex web of Middle Eastern geopolitics. Spanning approximately 9 kilometers and only about 100 meters wide, this corridor serves not only as a geographical boundary but also as a significant route for smuggling and military operations. Understanding the history and current dynamics of the Philadelphia Corridor is crucial for grasping the broader context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, particularly in light of recent military actions and political negotiations.
Historical Context of the Philadelphia Corridor
The origins of the Philadelphia Corridor date back to the 1979 peace accords between Egypt and Israel. This agreement resulted in the division of the city of Rafah, which is situated on either side of the border. Over the years, the stability of this area has fluctuated significantly, leading to numerous geopolitical tensions.
The 1979 Peace Accord
Presided over by U.S. President Jimmy Carter, the peace accord aimed to establish a framework for peace in the region. However, the subsequent years saw rising instability, particularly in Rafah:
- Egypt demolished its side of Rafah, creating a vacuum that allowed various groups to operate.
- Smuggling activities intensified, further complicating the security situation.
Israeli Military Operations
In response to increasing smuggling activities, the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) have made military incursions into the Philadelphia Corridor. This development has raised significant legal and diplomatic concerns, particularly regarding the violation of the 1978 accords.
Current Dynamics and Challenges
As the situation evolves, the Philadelphia Corridor remains a strategic area of concern for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. His administration’s primary goal has been to limit Hamas’s military capabilities while ensuring the security of Israel.
Challenges of Containing Hamas
Netanyahu’s strategy to curb Hamas’s rearming efforts faces multiple hurdles:
- Building an enduring military presence in Gaza is politically untenable.
- Alternative routes for arms smuggling, primarily through Egypt, are difficult to monitor.
- Ongoing negotiations with Hamas complicate military actions.
Role of International Actors
The involvement of the United States and other Arab states is crucial in facilitating a peaceful resolution. The potential for technology-based solutions to monitor and control smuggling activities is also being discussed, which could alleviate the need for a physical military presence.
The Path Forward: Military vs. Political Solutions
While military solutions seem necessary in the short term, they often exacerbate tensions and hinder long-term peace efforts. The focus must shift toward finding sustainable political solutions that address the root causes of the conflict.
Prospects for Peace
Achieving peace in the region requires:
- Security guarantees for both Israelis and Palestinians.
- Economic development initiatives to promote prosperity.
- International cooperation to mediate and monitor peace efforts.
Without these elements, the risk of recurring conflicts remains high, and future generations may continue to grapple with the same issues.
Conclusion
The Philadelphia Corridor serves as a microcosm of the broader Israeli-Palestinian conflict, highlighting the interplay between military action and political negotiation. As the region faces ongoing challenges, it is essential for leaders to prioritize sustainable solutions that foster peace and security for all parties involved. For further insights into the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, consider reading our related articles on [Middle Eastern Geopolitics](#) and [The Role of International Diplomacy](#).
“`